A French thinker named Michel de Montaigne described his nervousness and fear: “My lifestyles has been stuffed with horrible misfortunes, maximum of which by no means came about.” This quote captures the core of fear: the ordinary expectation that dreadful or catastrophic occasions will happen at some point and the implicit trust that troubling would possibly assist save you them from taking place.
Worries Ceaselessly Don’t Come True
Clinical proof suggests that the majority of our worries don’t come true. LaFreniere and Newman (2020) tracked the concerns of folks with generalized nervousness dysfunction (whose primary feature is power, difficult-to-control fear about quite a lot of subjects) and the way ceaselessly their worries got here true. They discovered that, on reasonable, folks had 34 distinct worries in a 10-day duration and that 91.4% of worries didn’t come true in a 30-day duration. That’s the common. The most typical quantity reported by way of the members was once 100%, that means that 100% of a given particular person’s worries didn’t come true. That’s to not say our worries by no means come true. Occasionally they do. Alternatively, on this learn about, even if the fear did come true, 30% of the concerns had been higher than anticipated.
This analysis touches upon two of the primary facets of tension: exaggerated expectancies of the probability that our worries (i.e., our feared results) will come true and the severity of the ones feared results in the event that they do come true (Berenbaum, Thompson, & Bredemeier, 2007; Berenbaum, Thompson, & Pomerantz, 2007; Dev, et al., 2024). Apparently, after we consider our feared result’s severity is prime, we ceaselessly overestimate the possibility that the dreaded result will happen (Berenbaum, Thompson, & Pomerantz, 2007).
As an example, consider there are two jars in entrance of you, every with 100 items of sweet. You get to select whether or not you wish to have to devour one randomly decided on piece of sweet from every jar. In every jar, 1 piece of sweet is poisoned. Within the first jar, the piece of poisoned sweet is mildly poisoned; should you occur to devour it, you could simply have a minor abdomen pain for 30 seconds. Alternatively, in the second one jar, should you occur to devour the poisoned sweet, it’ll be very critical, most likely deadly. You’ll be able to make a choice to devour sweet from jar 1, jar 2, each, or neither. How reluctant are you to devour one sweet from the primary jar? How about the second one jar? The percentages of having poisoned from both jar are objectively the similar: 1%. Alternatively, subjectively, does it really feel like the possibility of having the poisoned sweet is larger in jar 2 than jar 1 (i.e., if the sweet’s poison is critical vs delicate)? Almost definitely. In reality, in two research I carried out with my colleagues (Zbozinek, et al., 2021), we discovered that, when making choices, aversion to chance, loss, and ambiguity building up because the monetary worth of the selections building up. In different phrases, when the stakes are upper, we make extra wary choices.
Why Do We Fear?
If fear has a tendency to bias our predictions in regards to the probability and severity of doable damaging long run occasions, why can we fear, then? There are a pair causes. First, individuals who fear generally tend to have each sure and damaging ideals about their fear, and the sure ideals are those that take care of fear (Borkovec, Hazlett-Stevens, & Diaz, 1999; Borkovec, et al., 1983; Köcher, Schneider, & Christiansen, 2021; Wells, 1995). The damaging ideals are that fear is uncontrollable, ugly, and damaging. The sure ideals come with that fear prepares you for damaging results and stops them from happening. How ceaselessly do you fear since you consider it’ll assist save you issues at some point? 2d, fear is an avoidance technique. Along with seeking to keep away from long run damaging results, fear is a verbal procedure that reduces physiological activation (Hoehn-Saric & McLeod, 2000; Llera & Newman, 2010). When being concerned, we interact in fascinated about issues, which reduces our bodily emotions of tension or concern. Because of this it feels higher to fret than to really feel afraid or worried, so we now and again fear to scale back the emotional revel in of concern and nervousness.
Moreover, as I mentioned in a prior put up, concern and nervousness are elicited by way of eventualities that we consider are bad somehow, they usually encourage us to give protection to ourselves from the chance or keep away from it. In step with this, one theoretical and mathematical style of tension states that increased nervousness is related to over the top avoidance some distance upfront of doable threat (Zorowitz, Momennejad, & Daw, 2021). The theory right here is if threat can effectively be have shyed away from later, there is not any explanation why to keep away from it now (and there will also be prices to keeping off it now, like lacking out on relaxing facets of lifestyles, or attractive in annoying, effortful movements to keep away from the chance). Alternatively, worried individuals are much more likely to keep away from the chance some distance upfront of risk, which can result in out of place reliance on early avoidance, exaggerated ideals of threat, and generalization of concern since the particular person thinks they want to keep away from early and ceaselessly. This may result in fear and nervousness in protected eventualities, which is over the top, ugly, and will intervene with day by day lifestyles.
Moreover, as a result of fear is related to over the top avoidance, it’s necessary to remember the fact that fear has prices. It prices time, effort, and emotion. It may possibly even have dating prices: As an example, individuals who dislike uncertainty ceaselessly fear and search reassurance from relied on folks (Clark, et al., 2020). In small quantities, reassurance-seeking may well be wonderful, however over the top reassurance-seeking can pressure relationships (Halldorsson, et al., 2016; Shaver, Schachner, & Mikulincer, 2005). Reassurance-seeking additionally ends up in a reliance on others with the intention to really feel protected and disregards or reduces an individual’s skill to deal with issues on their very own. Fear too can have monetary prices (e.g., an individual who has worries about their well being would possibly excessively succeed in out to healthcare pros, subsequently incurring needless healthcare prices).
Drawback Fixing: The Wholesome Choice to Being worried
If being concerned is so expensive, what are we able to do as a substitute? The primary selection is drawback fixing. Each fear and drawback fixing goal to mend present issues or save you long run damaging results. Fear is perseverative and related to issue tolerating uncertainty (Koerner & Dugas, 2008), while drawback fixing is a lot more time- and effort-bound and efficient. (See Determine 1 for a conceptual representation.) Individuals who fear will seek for increasingly news associated with their drawback, searching for an answer and seeking to download sure bet that the verdict they’re making is the most productive one. Doing all of your analysis to determine a viable resolution is useful (a facet of drawback fixing), however with fear, the information-gathering procedure is unbounded and stretches past what is useful. The issue of worry-spurred news collecting is that the additional information you in finding, the much more likely the items of data are going to struggle with every different, which spurs additional news collecting. This ends up in numerous effort and time searching for one thing unattainable: sure bet in regards to the long run and sure bet that the selection being made is the most productive one. It additionally ends up in “research paralysis”—being beaten by way of the entire news and indecisive about how you can continue. Despite the fact that an individual comes up with a viable resolution whilst being concerned, they’ll most probably stay iterating excessively over the issue and the answer, like they’re caught in an unlimited loop.
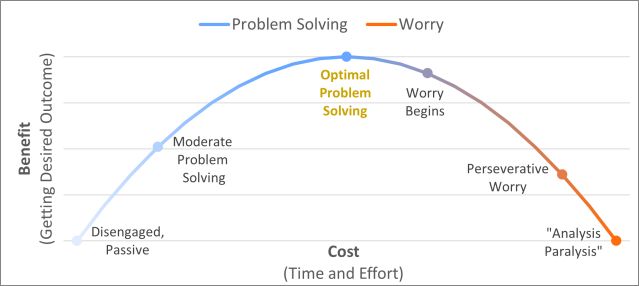
Determine 1. Drawback Fixing vs Fear: The Value-to-Receive advantages Ratio
Supply: Tomislav D. Zbozinek, PhD
By contrast, drawback fixing is a lot more environment friendly and concise. It does require some effort and time, however the effort and time shouldn’t be over the top, and drawback fixing typically yields really useful effects. Drawback fixing comes to defining the issue, pondering of answers, choosing an answer, enacting the answer, and transferring on (D’Zurilla & Nezu, 2010). If there are herbal ready sessions whilst enacting the answer (e.g., looking forward to a selected tournament to happen or to listen to again from any individual), an individual who’s being concerned will stay fascinated about the issue (with out making a lot growth), while an individual who’s drawback fixing will paintings on one thing else constructively (or interact in relaxing facets of lifestyles).
So, How Do I Prevent Being worried So A lot?
Step one is understanding the variation between drawback fixing and being concerned, as described above. The second one step is mindfulness, which is non-judgmental consciousness of the current second. Take note of when you find yourself being concerned. This implies consciously catching your self whilst you fear. A useful method to try this is to note when you find yourself feeling worried. Understand that you just’re feeling worried, and ask your self, “What was once I pondering proper ahead of I felt worried or whilst I used to be feeling worried?” This will likely permit you to determine the worrisome ideas. 3rd, consistent with cognitive behavioral remedy, worries are ideas, and ideas would possibly or is probably not correct, they usually would possibly or would possibly not come true. Remembering this whilst you understand your worrisome ideas can take the threshold off the ideas as a result of, although it might probably now and again really feel sure that worries will come true, it doesn’t imply they’ll. Fourth, shift from being concerned to drawback fixing, attractive in a extra restricted, intentional, and directed concept procedure to expand an answer, enact the answer, and transfer on. This may spare you heartaches and complications, all whilst serving to you extra successfully reach your targets. Finally, be told from this procedure. Did drawback fixing successfully permit you to reach your targets? Used to be it extra delightful than being concerned? Did any damaging results happen since you engaged in additional time-limited, effort-bound drawback fixing as a substitute of being concerned? Did sure results happen? With repeated apply, are you able to let pass of being concerned and as a substitute make drawback fixing your default?
Lowering fear can now and again be challenging. For individuals who fear so much, fear may well be routine, occur with out your consciousness, and be very resistant to switch. That is customary, so stay chipping away at your fear and seeking to substitute it with drawback fixing. As with maximum facets of tension, fear can also be nuanced, so addressing it might require figuring out the ones nuances and focused on them as it should be. If you are feeling like you could get pleasure from further assist, imagine attaining out to a reliable therapist for toughen; they may be able to in most cases permit you to determine ideals or patterns of pondering that give a contribution in your fear and permit you to fear much less.
To discover a therapist, consult with the Psychology Nowadays Remedy Listing.




























![VVS: Meet the Emerging K-Pop Woman Crew Set to Shine Like Diamonds [Teaser Images] – Kpoppie VVS: Meet the Emerging K-Pop Woman Crew Set to Shine Like Diamonds [Teaser Images] – Kpoppie](https://i1.wp.com/kpoppie.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/vvs-man-100.jpg?w=100&resize=100,100&ssl=1)






You must be logged in to post a comment Login